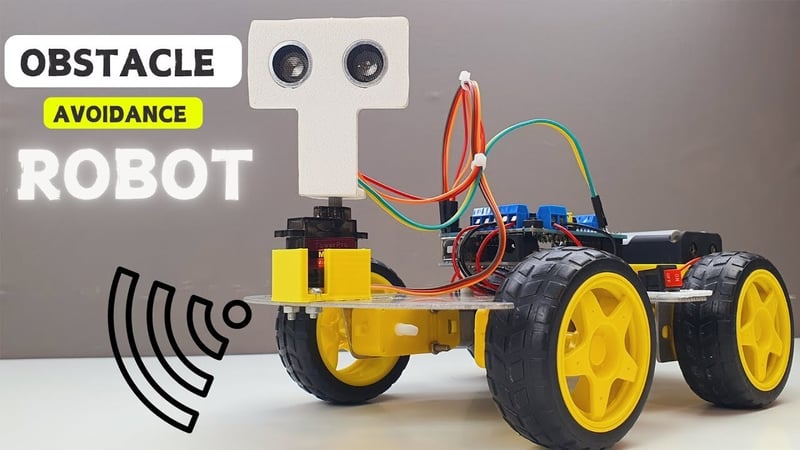
Creating an ultrasonic obstacle avoidance car using a single-chip microcontroller is a popular embedded systems project. The car uses an ultrasonic sensor to detect obstacles and adjusts its movement accordingly. Below is a step-by-step guide to designing and implementing this project:
1. System Overview
The system consists of:
- Microcontroller: Acts as the brain of the car (e.g., STM32, ESP32, Arduino, or PIC).
- Ultrasonic Sensor: Measures the distance to obstacles (e.g., HC-SR04).
- Motor Driver: Controls the motors for movement (e.g., L298N or TB6612FNG).
- DC Motors: Drive the wheels of the car.
- Power Supply: Provides power to the microcontroller, motors, and sensors.
2. Hardware Components
Microcontroller: STM32, ESP32, or Arduino.
Ultrasonic Sensor: HC-SR04.
Motor Driver: L298N or TB6612FNG.
DC Motors: Two or four motors for movement.
Chassis: A car chassis with wheels.
Power Supply: Batteries (e.g., 9V or 12V) and voltage regulators (e.g., 5V for the microcontroller).
Jumper Wires and Breadboard: For connections.
3. Circuit Design
- Ultrasonic Sensor Connection:
- VCC: Connect to 5V.
- GND: Connect to GND.
- Trig: Connect to a GPIO pin (e.g., PA0).
- Echo: Connect to another GPIO pin (e.g., PA1).
- Motor Driver Connection:
- IN1, IN2, IN3, IN4: Connect to GPIO pins (e.g., PB0, PB1, PB2, PB3).
- ENA, ENB: Connect to PWM-capable GPIO pins (e.g., PA8, PA9).
- VCC: Connect to the motor power supply (e.g., 9V).
- GND: Connect to GND.
- OUT1, OUT2, OUT3, OUT4: Connect to the DC motors.
- Power Supply:
- Use a voltage regulator (e.g., LM7805) to provide 5V to the microcontroller and sensors.
- Connect the motor power supply directly to the motor driver.
4. Software Design
Step 1: Initialize Peripherals
- Configure GPIO pins for the ultrasonic sensor and motor driver.
- Set up timers for PWM (to control motor speed).
Step 2: Measure Distance
- Use the ultrasonic sensor to measure the distance to obstacles.
- Send a 10µs pulse to the Trig pin.
- Measure the pulse width on the Echo pin to calculate the distance.
Step 3: Control Motors
- Use the motor driver to control the direction and speed of the motors.
- Implement functions for forward, backward, left, right, and stop movements.
Step 4: Implement Obstacle Avoidance Logic
- If an obstacle is detected within a certain distance (e.g., 20 cm), stop or reverse the car.
- Turn left or right to avoid the obstacle.
5. Example Code (STM32CubeIDE)
Ultrasonic Sensor Code
c
#include "stm32f4xx_hal.h"
#define TRIG_PIN GPIO_PIN_0
#define TRIG_PORT GPIOA
#define ECHO_PIN GPIO_PIN_1
#define ECHO_PORT GPIOA
uint32_t get_distance(void) {
// Send 10µs pulse to Trig pin
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(TRIG_PORT, TRIG_PIN, GPIO_PIN_SET);
HAL_Delay(0.01); // 10µs delay
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(TRIG_PORT, TRIG_PIN, GPIO_PIN_RESET);
// Measure pulse width on Echo pin
uint32_t start_time = 0, end_time = 0;
while (HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(ECHO_PORT, ECHO_PIN) == GPIO_PIN_RESET);
start_time = HAL_GetTick();
while (HAL_GPIO_ReadPin(ECHO_PORT, ECHO_PIN) == GPIO_PIN_SET);
end_time = HAL_GetTick();
// Calculate distance (in cm)
uint32_t pulse_width = end_time - start_time;
uint32_t distance = pulse_width * 0.034 / 2; // Speed of sound = 340 m/s
return distance;
}
Motor Control Code
c
void move_forward(void) {
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_SET); // IN1
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN2
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_2, GPIO_PIN_SET); // IN3
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_3, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN4
}
void move_backward(void) {
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN1
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_SET); // IN2
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_2, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN3
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_3, GPIO_PIN_SET); // IN4
}
void turn_left(void) {
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN1
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_SET); // IN2
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_2, GPIO_PIN_SET); // IN3
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_3, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN4
}
void turn_right(void) {
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_SET); // IN1
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN2
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_2, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN3
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_3, GPIO_PIN_SET); // IN4
}
void stop(void) {
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_0, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN1
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_1, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN2
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_2, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN3
HAL_GPIO_WritePin(GPIOB, GPIO_PIN_3, GPIO_PIN_RESET); // IN4
}
Main Code
c
int main(void) {
HAL_Init();
SystemClock_Config();
GPIO_Init();
while (1) {
uint32_t distance = get_distance();
if (distance < 20) { // Obstacle detected
stop();
HAL_Delay(500);
move_backward();
HAL_Delay(500);
turn_left();
HAL_Delay(500);
} else { // No obstacle
move_forward();
}
}
}
6. Testing and Debugging
- Test the Ultrasonic Sensor:
Verify that the sensor accurately measures distance.
- Test Motor Control:
Ensure the motors move in the correct direction and speed.
- Test Obstacle Avoidance:
Place obstacles in front of the car and verify that it avoids them.
7. Enhancements
- Add Speed Control:
Use PWM to control motor speed.
- Add Multiple Sensors:
Use multiple ultrasonic sensors for better obstacle detection.
- Add Bluetooth/Wi-Fi Control:
Use an ESP32 to add remote control via a smartphone app.
- Add Display:
Use an LCD or OLED to display distance and status.
By following these steps, you can build an ultrasonic obstacle avoidance car using a single-chip microcontroller.



Top comments (0)