In this tutorial, we will use AWS services to create a serverless application for a coffee shop. The user (coffee shop owner in this case) can authenticate using AWS Cognito and manage inventory (perform CRUD operations).
Github Repo: https://github.com/TrickSumo/AWS-CRUD-Serverless
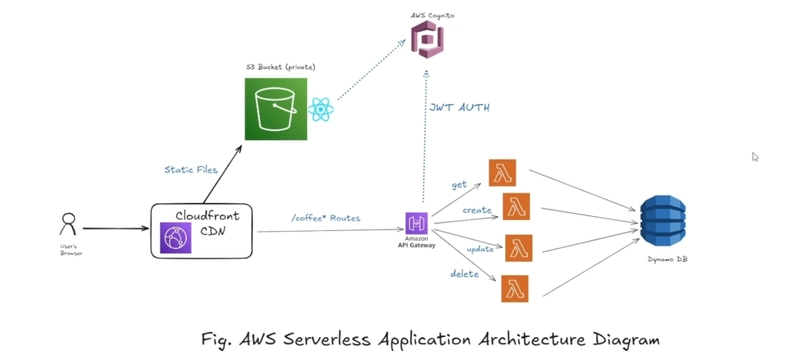
Architecture Overview
We will use DynamoDB to store data and lambda functions (with lambda layer) to process API gateway requests. API gateway will be secured by Cognito and exposed with the help of Cloudfront CDN. React frontend will also be configured with Cognito UserPool and hosted on S3 and Cloudfront.
Optionally, Cloudflare and AWS Certificate Manager can be used to add a custom domain to Cloudront distribution.
Step 1 – Create DynamoDB Table
Head over to the AWS console and navigate to the DynamoDB section. Then create a new table with table name as “CoffeeShop” and partiton key as “coffeeId”.
Create a new item (coffee) in the table and fill attributes like coffeeId, name, price, and availability. It will be helpful to test connectivity to DynamoDB.
{
"coffeeId": "c123",
"name": "new cold coffee",
"price": 456,
"available": true
}
Step 2 – Create IAM Role For Lambda Function
Create a new IAM role with permissions to create CloudWatch logs and CRUD access to the “CoffeeShop” DynamoDB table. Let us call this IAM role as “CoffeeShopRole” and its a generic role for all our lambda functions.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "VisualEditor0",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"dynamodb:PutItem",
"dynamodb:DeleteItem",
"dynamodb:GetItem",
"dynamodb:Scan",
"dynamodb:UpdateItem"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:dynamodb::<DYNAMODB_TABLE_NAME>"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"logs:CreateLogGroup",
"logs:CreateLogStream",
"logs:PutLogEvents"
],
"Resource": "*"
}
]
}
Step 3: Create Lambda Layer And Lambda Functions
First, create a Node.js Lambda layer that includes the DynamoDB library and common utility functions. It will help us avoid redundant installations of the same dependencies across multiple Lambdas.
mkdir nodejs
cd nodejs
npm init
npm i @aws-sdk/client-dynamodb @aws-sdk/lib-dynamodb
touch utils.mjs
Now create a utils.mjs file to keep the code for DynamoDB client initialization and createResponse function.
import { DynamoDBClient } from "@aws-sdk/client-dynamodb";
import {
DynamoDBDocumentClient,
ScanCommand,
GetCommand,
PutCommand,
UpdateCommand,
DeleteCommand
} from "@aws-sdk/lib-dynamodb";
const client = new DynamoDBClient({});
const docClient = DynamoDBDocumentClient.from(client);
const createResponse = (statusCode, body) => {
return {
statusCode,
headers: { "Content-Type": "application/json" },
body: JSON.stringify(body),
};
};
export {
docClient,
createResponse,
ScanCommand,
GetCommand,
PutCommand,
UpdateCommand,
DeleteCommand
};
Then, create a zip of the content and upload it in a new lambda layer. According to convention, the folder where we keep all these dependencies must be named “nodejs”. Apart from that, the name of the zip file and lambda layer can be anything.
In our case, let us create zip named “layer.zip” and upload it to the Lambda layer named “Dynamo-Layer”
cd ..
zip -r layer.zip nodejs
Now create four lambda functions and attach this layer (Dynamo-Layer) and IAM Role (CoffeeShopRole) to them.
// getCoffee Function
import { docClient, GetCommand, ScanCommand, createResponse } from '/opt/nodejs/utils.mjs'; // Import from Layer
const tableName = process.env.tableName || "CoffeeShop";
export const getCoffee = async (event) => {
const { pathParameters } = event;
const { id } = pathParameters || {};
try {
let command;
if (id) {
command = new GetCommand({
TableName: tableName,
Key: {
"coffeeId": id,
},
});
}
else {
command = new ScanCommand({
TableName: tableName,
});
}
const response = await docClient.send(command);
return createResponse(200, response);
}
catch (err) {
console.error("Error fetching data from DynamoDB:", err);
return createResponse(500, { error: err.message });
}
}
// createCoffee Function
import { docClient, PutCommand, createResponse } from '/opt/nodejs/utils.mjs'; // Import from Layer
const tableName = process.env.tableName || "CoffeeShop";
export const createCoffee = async (event) => {
const { body } = event;
const { coffeeId, name, price, available } = JSON.parse(body || "{}");
console.log("valuies", coffeeId, name, price, available);
if (!coffeeId || !name || !price || available === undefined) {
return createResponse(409, { error: "Missing required attributes for the item: coffeeId, name, price, or available." });
}
const command = new PutCommand({
TableName: tableName,
Item: {
coffeeId,
name,
price,
available
},
ConditionExpression: "attribute_not_exists(coffeeId)",
});
try {
const response = await docClient.send(command);
return createResponse(201, { message: "Item Created Successfully!", response });
}
catch (err) {
if (err.message === "The conditional request failed")
return createResponse(409, { error: "Item already exists!" });
else
return createResponse(500, {
error: "Internal Server Error!",
message: err.message,
});
}
}
// updateCoffee Function
import { docClient, UpdateCommand, createResponse } from '/opt/nodejs/utils.mjs'; // Import from Layer
const tableName = process.env.tableName || "CoffeeShop";
export const updateCoffee = async (event) => {
const { pathParameters, body } = event;
const coffeeId = pathParameters?.id;
if (!coffeeId)
return createResponse(400, { error: "Missing coffeeId" });
const { name, price, available } = JSON.parse(body || "{}");
if (!name && !price && available === undefined)
return createResponse(400, { error: "Nothing to update!" })
let updateExpression = `SET ${name ? "#name = :name, " : ""}${price ? "price = :price, " : ""}${available ? "available = :available, " : ""}`.slice(0, -2);
try {
const command = new UpdateCommand({
TableName: tableName,
Key: {
coffeeId,
},
UpdateExpression: updateExpression,
...(name && {
ExpressionAttributeNames: {
"#name": "name", // name is a reserved keyword in DynamoDB
},
}),
ExpressionAttributeValues: {
...(name && { ":name": name }),
...(price && { ":price": price }),
...(available && { ":available": available }),
},
ReturnValues: "ALL_NEW", // returns updated value as response
ConditionExpression: "attribute_exists(coffeeId)", // ensures the item exists before updating
});
const response = await docClient.send(command);
console.log(response);
return response;
}
catch (err) {
if (err.message === "The conditional request failed")
return createResponse(404, { error: "Item does not exists!" });
return createResponse(500, {
error: "Internal Server Error!",
message: err.message,
});
}
}
// deleteCoffee Function
import { docClient, DeleteCommand, createResponse } from '/opt/nodejs/utils.mjs'; // Import from Layer
const tableName = process.env.tableName || "CoffeeShop";
export const deleteCoffee = async (event) => {
const { pathParameters } = event;
const coffeeId = pathParameters?.id;
if (!coffeeId)
return createResponse(400, { error: "Missing coffeeId" });
try {
const command = new DeleteCommand({
TableName: tableName,
Key: {
coffeeId,
},
ReturnValues: "ALL_OLD", // returns deleted value as response
ConditionExpression: "attribute_exists(coffeeId)", // ensures the item exists before deleting
});
const response = await docClient.send(command);
return createResponse(200, { message: "Item Deleted Successfully!", response });
}
catch (err) {
if (err.message === "The conditional request failed")
return createResponse(404, { error: "Item does not exists!" });
return createResponse(500, {
error: "Internal Server Error!",
message: err.message,
});
}
}
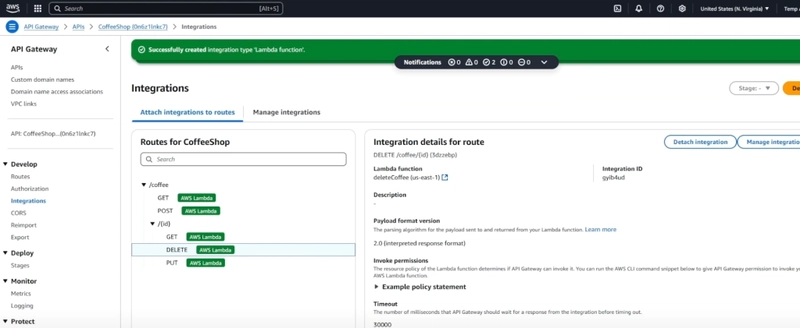
Step 4: Create API Gateway To Expose Lambda Functions
Create an HTTP API Gateway and add five routes pointing to the above lambda functions.
GET /coffee -> getCoffee lambda function
GET /coffee/{id} -> getCoffee lambda function
POST /coffee -> createCoffee lambda function
PUT /coffee/{id} -> updateCoffee lambda function
DELETE /coffee/{id} -> deleteCoffee lambda function
At this point, you should be able to use all APIs using Postman or Thunderclient.
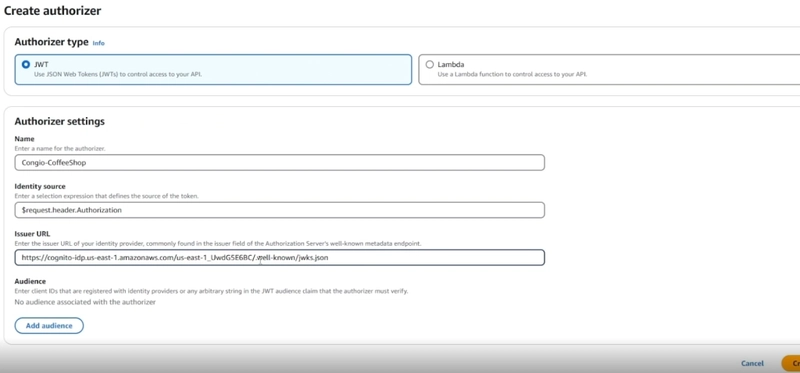
Step 5: Create Cognito UserPool And API Gateway Authorizer
Create a cognito UserPool with a public client (SPA App) and use it as a JWT authorizer for API gateway for all the routes.
Step 6: Setup React Application And Upload Build To S3 Bucket
Create a new React app and configure it with Cognito. You can copy files from here: https://github.com/TrickSumo/AWS-CRUD-Serverless/tree/main/FrontendWithAuth
Create a new S3 bucket, build the React app, and upload the “dist” folder to the S3 bucket.
Step 7: Create Cloudfront Distribution With Behaviors For S3 And API Gateway
Create a new Cloudfront distribution with S3 as the origin and use OAC to access the private bucket (make sure to update bucket policy).
Create another origin pointing to API gateway and create a new behaviour to redirect “/coffee*” routes to this new origin.
Step 8: Attach Custom Domain Name To CDN (Optional)
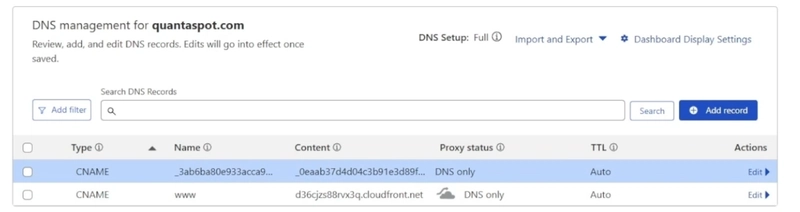
Edit CDN settings to add an alternate domain name. Use AWS Certificate Manager to issue an SSL certificate (to verify domain ownership, CNAME record method can be used).
Create a new CNAME record from the domain name control panel to point to the Cloudfront distribution URL.
Done 🥳
Step 9: Clean Up All Resources
Now it’s time to clear all resources. Delete CDN, DynamoDB, API Gateway, Lambdas (with Layer), IAM Role, ACM certificate, and Cognito UserPool.
Hope you enjoyed the tutorial! Thanks 🙂



Top comments (5)
Amazing guide! This tutorial presents steps for creating a robust serverless app seamlessly.
Thanks :)
Knowledgeable, thanks <3
Make use of AWS Amplify . It reduces a lot manual code intervention regarding Cognito DynamoDB ,lambda and API Gateway
Agree! Amplify or frameworks like Serverless/SST reduce manual intervention a lot. And best for development.
But in this post, I wanted to show behind the scenes without any abstractions. That's why manually created everything.
Amplify is on my to-learn list, will check it out. Thanks ☺️